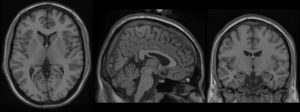
Stereotaxic Registration Model, original 1998 version
However, the high definition proved too attractive to the community and, after non-linear mapping to fit the MNI305 space, it has been adopted by many groups as a stereotaxic template (e.g., AFNI, Cox,; Brainstorm, Tadel et al., 2011; SPM, Litvak et al., 2011; Fieldtrip, Oostenveld et al., 2011).
Methods
This average dataset was created in a two step process. First, each of the 27 T1-weighted scans were registered to stereotaxic space using the mritotal procedure and resampled onto a 1mm grid in stereotaxic space. All 27 scans were averaged together to create an initial average. This average volume was used as a target for the second phase of registration where each original T1-weighted MRI was re-registered in stereotaxic space. This procedure has the advantage of removing the small variance in intra-subject mapping in stereotaxic space associated with the use of a multi-subject average.
Holmes CJ, Hoge R, Collins L, Woods R, Toga AW, Evans AC. “Enhancement of MR images using registration for signal averaging.” J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1998 Mar-Apr;22(2):324–33. https://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00004728-199803000-00032
License
Copyright (C) 1993–2009 Louis Collins, McConnell Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University. Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software and its documentation for any purpose and without fee is hereby granted, provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies. The authors and McGill University make no representations about the suitability of this software for any purpose. It is provided “as is” without express or implied warranty. The authors are not responsible for any data loss, equipment damage, property loss, or injury to subjects or patients resulting from the use or misuse of this software package.
Download
Download archives containing average t1w scan, brain mask and head mask: MINC1 13MB MINC2 13MB NIFTI 24MB